

The presence of FTSW should alert clinicians to the possibility of an underlying chronic and/or static CNS pathology, in particular congenital CNS anomalies, underscoring the significance of neuroimaging in the work-up of this population. Even though more than one mechanism may be involved in the pathogenesis of FTSW, we believe a deeply seated pacemaker as the source of this EEG pattern is the most compelling theory. We were surprised to find that half of the patients with FTSW had chronic and/or static CNS pathology, particularly congenital CNS anomalies. The majority of these patients responded favorably to anticonvulsant monotherapy. Ninety percent of the patients with FTSW had epilepsy, presenting clinically with generalized convulsive seizures, often without partial onset. Our data revealed that FTSW were rare EEG events occurring primarily in the first two decades of life. This investigation was conducted on a heterogeneous group of patients at KKH, Ha’il, KSA. We will discuss this EEG pattern with respect to its clinical, neurophysiological, and neuropathological significance. In this paper, we will address the significance of prominent (high amplitude) ASW, giving rise to a triphasic morphology of the IED (focal triphasic sharp waves and spikes-FTSW). Surprisingly, however, little attention has been drawn to the after-coming slow wave (ASW), and its pathological as well as clinical significance. Posterior-predominant delta activity in this case is probably due to the predominant involvement of posterior head region in PRES.There is a plethora of data in the EEG literature on the characteristics of the most prominent component of interictal epileptiform discharges (IED), namely the negative (fast) phase. Polymorphic delta comas are due to structural abnormalities involving subcortical white matter or profound metabolic coma. With progression to deeper stages of coma, it appears diffuse and is usually unreactive. 1 The delta coma EEG pattern is usually seen with more advanced states of encephalopathy and coma. The patient recovered after cyclophosphamide was stopped, and the blood pressure was well controlled.ĭiffuse slowing is the most common finding on the EEGs in posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome (PRES). Head CT and MRI show diffuse white matter involvement, maximally expressed in the watershed areas in the two hemispheres. EEG shows continuously diffuse polymorphic delta activity (PDA) with occipital predominance. After the visual hallucination, she was found to have elevation of her blood pressure. A 10-year-old girl with microscopic polyangiitis and chronic renal failure developed visual hallucinations, lethargy, and new-onset seizures.
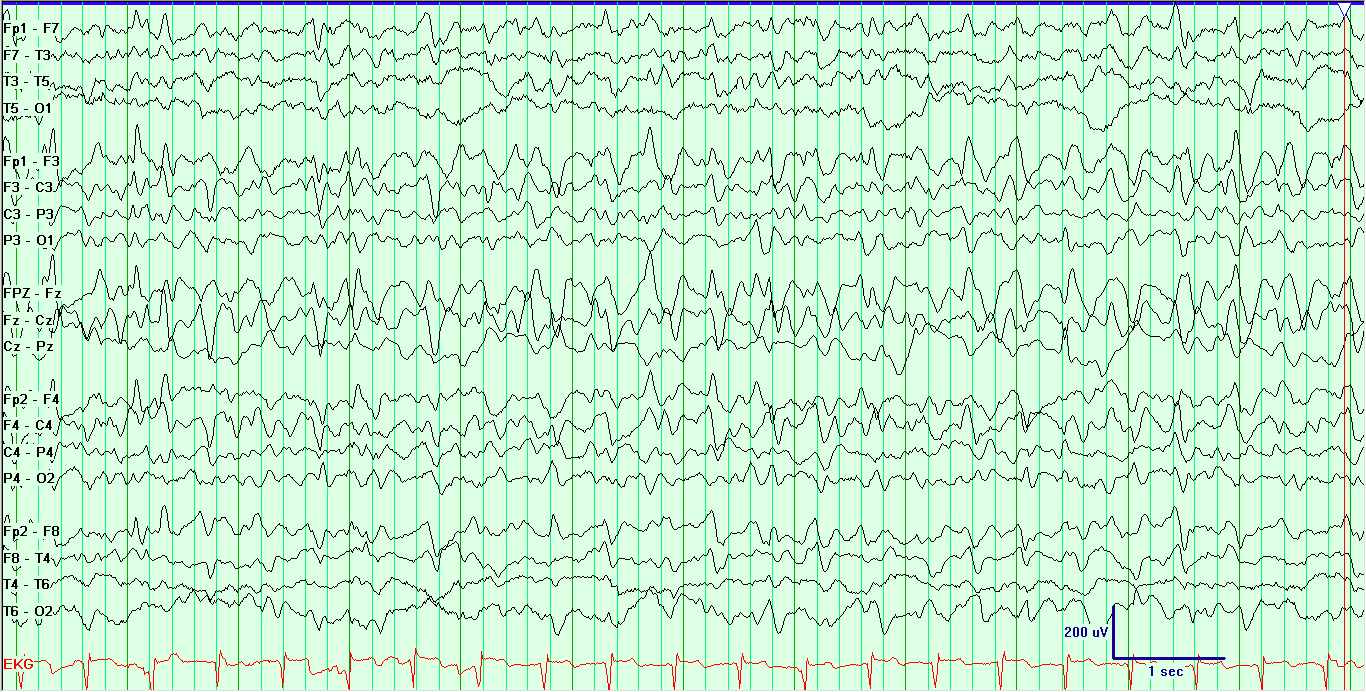
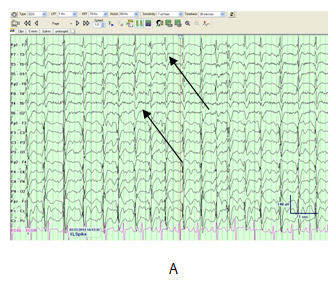
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES) Diffuse Polymorphic Delta Activity with Posterior Predominance.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
